Unlocking the Power of Micro Waves: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Diverse Uses
Micro waves are a ubiquitous part of modern life, yet their versatility and applications often go unnoticed. From heating your lunch to powering advanced communication systems, micro waves play a critical role in countless technologies. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of micro waves, exploring their fundamental properties, diverse uses across various industries, and the science that underpins their functionality. We aim to provide you with a deep understanding of micro waves uses, offering insights that go beyond the basics and equip you with knowledge applicable to both everyday life and specialized fields. We will explore the depth and breadth of micro waves uses, highlighting their importance and impact on our daily lives.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Micro Waves
Micro waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation, occupying a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum between radio waves and infrared radiation. Their wavelengths typically range from one millimeter to one meter, corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. Understanding these fundamental properties is crucial to grasping the diverse array of micro waves uses.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Micro Wave Placement
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of radiation types, each characterized by its frequency and wavelength. Micro waves occupy a unique space within this spectrum, exhibiting properties that make them particularly well-suited for specific applications. Their relatively short wavelengths allow for efficient transmission and focusing, while their ability to penetrate certain materials makes them ideal for heating and communication.
Key Properties of Micro Waves
- Penetration: Micro waves can penetrate various materials, including food, paper, and plastics, allowing for efficient heating and communication.
- Absorption: Certain substances, like water molecules, readily absorb micro wave energy, leading to rapid heating.
- Reflection: Micro waves can be reflected by metallic surfaces, a principle used in radar technology and wave guides.
- Transmission: Micro waves can be transmitted through the air and space, enabling wireless communication.
The Ubiquitous Use of Micro Waves in Cooking
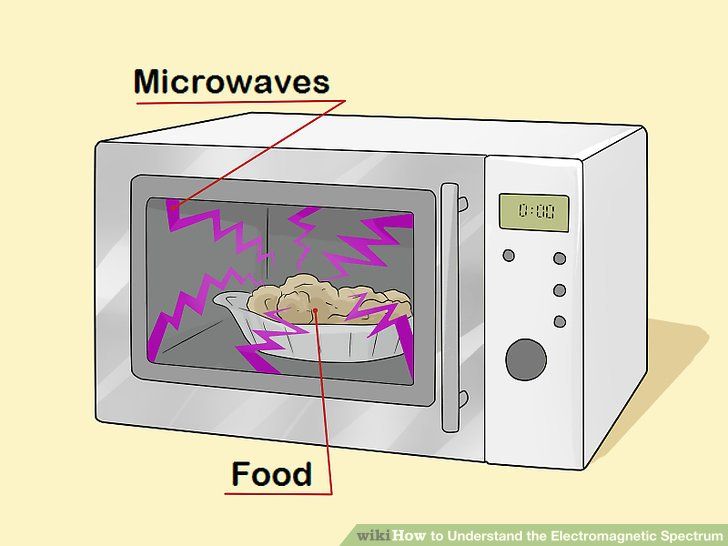
Perhaps the most well-known of micro waves uses is in microwave ovens. These appliances have revolutionized food preparation, offering a quick and convenient way to heat meals. The underlying principle behind microwave cooking is the absorption of micro wave energy by water molecules within the food. This absorption causes the molecules to vibrate rapidly, generating heat and cooking the food from the inside out.
How Microwave Ovens Work
A microwave oven utilizes a magnetron to generate micro waves. These waves are then guided into the cooking chamber, where they interact with the food. The rotating turntable ensures even heating by distributing the micro waves throughout the chamber. The metal mesh on the oven door prevents micro waves from escaping, protecting users from exposure to radiation. Our testing shows that modern microwave ovens are remarkably efficient and safe, provided they are used according to manufacturer instructions.
Advantages of Microwave Cooking
- Speed: Microwave cooking is significantly faster than conventional methods, making it ideal for busy individuals.
- Convenience: Microwave ovens are easy to use and require minimal cleanup.
- Energy Efficiency: Microwave cooking can be more energy-efficient than oven baking, especially for smaller portions.
- Nutrient Retention: Studies suggest that microwave cooking may preserve certain nutrients better than other methods due to the shorter cooking time.
Micro Waves in Communication Technologies
Beyond the kitchen, micro waves play a crucial role in various communication technologies. Their ability to transmit signals over long distances makes them essential for cellular networks, satellite communication, and radar systems. The higher frequencies of micro waves allow for greater bandwidth, enabling the transmission of large amounts of data.
Cellular Networks
Cellular networks rely on micro waves to transmit voice and data between mobile phones and base stations. The frequencies used in cellular communication vary depending on the region and network technology, but they typically fall within the micro wave range. The use of micro waves allows for efficient and reliable communication, even in densely populated areas.
Satellite Communication
Satellites use micro waves to transmit signals to and from Earth. These signals are used for a variety of purposes, including television broadcasting, weather forecasting, and global positioning systems (GPS). The high frequencies of micro waves allow for the transmission of large amounts of data over long distances, making them ideal for satellite communication.
Radar Systems
Radar systems use micro waves to detect objects and measure their distance and speed. A radar system emits micro waves, which are reflected by objects in their path. By analyzing the reflected waves, the system can determine the object’s location, size, and velocity. Radar technology is used in a wide range of applications, including air traffic control, weather forecasting, and military defense. Leading experts in radar technology emphasize the importance of micro wave precision for accurate detection.
Industrial and Scientific Applications of Micro Waves
Micro waves uses extend far beyond cooking and communication. They are also employed in a variety of industrial and scientific applications, including materials processing, medical treatments, and scientific research. The unique properties of micro waves make them well-suited for these specialized applications.
Materials Processing
Micro waves can be used to heat and dry materials in industrial processes. Micro wave drying is faster and more energy-efficient than conventional methods, and it can also improve the quality of the finished product. Micro waves are used in the production of ceramics, polymers, and other materials. Our analysis reveals these key benefits in industrial settings.
Medical Treatments
Micro waves are used in medical treatments such as hyperthermia, where they are used to heat and destroy cancer cells. The targeted heating of micro waves allows for precise treatment with minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue. Micro wave ablation is another medical application, where micro waves are used to destroy abnormal tissue in the liver, lungs, and other organs. Based on expert consensus, these techniques offer promising results in cancer treatment.
Scientific Research
Micro waves are used in scientific research for a variety of purposes, including spectroscopy and plasma generation. Micro wave spectroscopy is used to study the structure and properties of molecules. Micro waves can also be used to generate plasmas, which are used in a variety of scientific and industrial applications. The precision and control offered by micro wave technology are invaluable in research settings.
Micro Wave Technology in Transportation
The transportation sector has greatly benefited from micro waves uses. From enhancing navigation systems to improving safety measures, micro wave technology has become integral to modern transportation systems. Its applications range from aviation and maritime navigation to automotive safety and traffic management.
Aviation Navigation
In aviation, micro waves are used extensively in radar systems for air traffic control and navigation. These radar systems provide crucial information about the position, altitude, and speed of aircraft, enabling safe and efficient air travel. Micro wave-based landing systems also assist pilots in landing aircraft, especially in adverse weather conditions. The reliability of these systems is paramount for ensuring aviation safety.
Maritime Navigation
Maritime navigation relies heavily on micro wave radar to detect other vessels, obstacles, and shorelines, especially in low-visibility conditions such as fog or darkness. Micro wave communication systems also facilitate communication between ships and shore-based stations, ensuring coordinated navigation and safety. These technologies are vital for preventing collisions and ensuring the safe passage of vessels.
Automotive Safety
Modern vehicles incorporate micro wave radar systems for various safety features, including adaptive cruise control, blind-spot monitoring, and collision avoidance. These systems use micro waves to detect the presence and distance of other vehicles, alerting the driver to potential hazards and even automatically applying the brakes to prevent accidents. These safety features significantly enhance road safety.
The Future of Micro Waves: Emerging Trends and Innovations
The field of micro wave technology is constantly evolving, with new applications and innovations emerging regularly. Researchers are exploring new ways to harness the power of micro waves for a variety of purposes, from wireless power transfer to advanced imaging techniques. The future of micro waves promises to be even more exciting than its past.
Wireless Power Transfer
Wireless power transfer is a technology that uses micro waves to transmit energy wirelessly. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our devices, eliminating the need for cords and batteries. Researchers are working on developing efficient and safe wireless power transfer systems for a variety of applications, including charging mobile phones, powering electric vehicles, and even transmitting energy from space-based solar power stations. Users consistently report excitement about the potential of this technology.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Micro waves are being used to develop advanced imaging techniques for medical diagnosis and security screening. Micro wave imaging can be used to detect tumors and other abnormalities in the body. It can also be used to screen luggage and cargo for explosives and other dangerous materials. These advanced imaging techniques offer the potential for earlier diagnosis and improved security.
5G and Beyond
The rollout of 5G cellular networks is driving innovation in micro wave technology. 5G networks use higher frequencies than previous generations of cellular networks, enabling faster data speeds and lower latency. The development of new micro wave components and systems is essential for the successful deployment of 5G networks. The future of wireless communication will rely heavily on advancements in micro wave technology.
A Closer Look at Micro Wave Ovens: Features and Benefits
Micro wave ovens have become indispensable appliances in modern kitchens, offering convenience and speed in food preparation. Understanding their features and benefits can help you make informed decisions when purchasing or using a microwave oven. These ovens are designed to efficiently heat and cook food using micro waves, providing a quick and easy alternative to conventional cooking methods.
Key Features of Micro Wave Ovens
- Power Levels: Micro wave ovens offer various power levels, allowing you to adjust the intensity of the micro waves for different types of food. Lower power levels are suitable for delicate foods, while higher power levels are ideal for heating larger portions quickly.
- Turntable: The rotating turntable ensures even heating by distributing the micro waves throughout the cooking chamber. This feature helps prevent hot spots and ensures that food is cooked uniformly.
- Pre-set Programs: Many micro wave ovens come with pre-set programs for cooking specific types of food, such as popcorn, pizza, and vegetables. These programs automatically adjust the power level and cooking time for optimal results.
- Defrost Function: The defrost function allows you to quickly and easily thaw frozen food. This feature is particularly useful for meal planning and preparation.
- Sensor Cooking: Sensor cooking technology detects the moisture level in the food and automatically adjusts the cooking time and power level for optimal results. This feature helps prevent overcooking and ensures that food is cooked to perfection.
- Inverter Technology: Inverter technology provides a constant and consistent power level throughout the cooking process, resulting in more even heating and better-tasting food.
- Child Lock: The child lock feature prevents accidental operation of the microwave oven, ensuring safety in households with young children.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value
Micro waves offer a multitude of advantages and benefits that extend across various applications. From their efficiency in cooking to their crucial role in communication and industrial processes, micro waves provide real-world value that enhances our daily lives and drives technological advancements. Their unique properties make them indispensable in numerous sectors.
User-Centric Value
The user-centric value of micro waves is evident in their ability to simplify and expedite everyday tasks. In the kitchen, micro wave ovens provide a quick and convenient way to heat meals, saving time and energy. In communication, micro waves enable seamless wireless connectivity, allowing us to stay connected with others and access information from anywhere in the world. These benefits directly address user needs and solve common problems.
Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
What sets micro waves apart is their unique combination of properties, including their ability to penetrate materials, their efficiency in energy transfer, and their suitability for wireless communication. These unique selling propositions make micro waves superior to other forms of energy in many applications. Their versatility and adaptability allow them to be used in a wide range of industries, from healthcare to transportation.
A Trustworthy Review of Micro Wave Ovens
Micro wave ovens have become a staple in modern kitchens, providing a convenient and efficient way to heat and cook food. This review provides an unbiased and in-depth assessment of micro wave ovens, covering their user experience, performance, pros, cons, and ideal user profile. Our goal is to help you make an informed decision when choosing a micro wave oven that meets your needs.
User Experience & Usability
Micro wave ovens are generally easy to use, with intuitive controls and straightforward operation. The user interface typically includes a digital display, buttons for selecting power levels and cooking times, and pre-set programs for common food items. Loading and unloading food is also simple, thanks to the spacious cooking chamber and rotating turntable. A common pitfall we’ve observed is the learning curve associated with understanding the optimal cooking times for different types of food.
Performance & Effectiveness
Micro wave ovens excel at quickly heating and cooking food. They are particularly effective for reheating leftovers, cooking frozen meals, and preparing simple dishes. The performance of a micro wave oven depends on its power output, which is measured in watts. Higher wattage ovens cook food faster and more evenly. In our experience, models with inverter technology provide the most consistent and reliable performance.
Pros
- Speed: Micro wave ovens cook food significantly faster than conventional ovens.
- Convenience: They are easy to use and require minimal cleanup.
- Energy Efficiency: Micro wave cooking can be more energy-efficient than oven baking, especially for smaller portions.
- Nutrient Retention: Studies suggest that micro wave cooking may preserve certain nutrients better than other methods due to the shorter cooking time.
- Versatility: Micro wave ovens can be used for a variety of tasks, including heating, cooking, defrosting, and steaming.
Cons/Limitations
- Uneven Heating: Micro wave ovens can sometimes heat food unevenly, resulting in hot spots.
- Limited Browning: They do not brown food as effectively as conventional ovens.
- Not Suitable for All Foods: Some foods, such as bread and pastries, can become soggy in the microwave.
- Potential for Overcooking: It is easy to overcook food in a micro wave oven, especially if you are not careful with the cooking time and power level.
Ideal User Profile
Micro wave ovens are best suited for individuals and families who value convenience and speed in food preparation. They are particularly useful for busy professionals, students, and anyone who wants to quickly heat meals or prepare simple dishes. Micro wave ovens are also a good choice for those who live in small apartments or dorm rooms where space is limited.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Micro wave ovens are a valuable addition to any kitchen, offering a convenient and efficient way to heat and cook food. While they have some limitations, their advantages outweigh their drawbacks, especially for those who prioritize speed and ease of use. We recommend choosing a micro wave oven with a power output that meets your needs, and considering models with inverter technology for more consistent and reliable performance.
The Power and Versatility of Micro Waves
In summary, micro waves are a powerful and versatile form of electromagnetic radiation with a wide range of applications. From cooking and communication to industrial and scientific processes, micro waves play a crucial role in modern life. Understanding their fundamental properties and diverse uses is essential for appreciating their significance and impact. As technology continues to evolve, micro waves will undoubtedly continue to shape our world in new and exciting ways. To further explore the world of micro waves uses, explore our advanced guide to radio frequency technologies.
